Motivation
Camera-based sensors offer affordable sensing in public spaces and hence, they have become particularly important in many autonomous systems, surveillance, and traffic applications. However, in trying to be robust and adaptive to a variety of scenarios, the existing techniques are highly computationally intensive. Most of the existing solutions either rely on cloud-based computing, where the raw video data from all cameras is sent to the server for processing and analysis, or very expensive edge-computing and smart camera-based solutions. Neither of these options are scalable for large-scale deployment. Furthermore, due to privacy concerns, it is prohibitive to send raw video data from the camera sensors to a central location for visual analytics using cloud-grade GPUs. In addition, localized processing is critical for ensuring a high level of responsiveness of the system.
Our research investigates novel architecture-aware algorithms and design methodologies that can lead to low-complexity and real-time visual analytics for deployment on edge devices with tight computational constraints.
The following are some of our projects in this area:
Fast and Accurate Pedestrian Detection
There is now a stricter requirement from government and society to protect vulnerable traffic participants. The pedestrian detection system in automotive industry is expected to record a CAGR of over 15% during the forecast period (2020 - 2025). The current pandemic also creates an urgent demand for automated systems that can enforce social distancing (e.g., people counting and measuring the distance between humans in public areas).
We proposed a multi-task deep learning architecture that inter-fuse the task of pedestrian/human detection and semantic segmentation to improve the accuracy of detecting pedestrians. Unlike existing methods, the proposed architecture can effectively detect occluded pedestrians and small pedestrians (i.e., pedestrians who are located at a far distance from the camera).
The computational complexity of the proposed pedestrian detection algorithm is very low which enables it to run on embedded platforms with low computational resources at high-speed. As such, it is suitable for edge computing to maintain privacy of the detected people. The proposed architecture can also achieve high detection performance with low resolution input images, which significantly reduces the computational complexity. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art detection performance on widely-used pedestrian detection dataset, and runs about 3X faster than state-of-the-art methods.
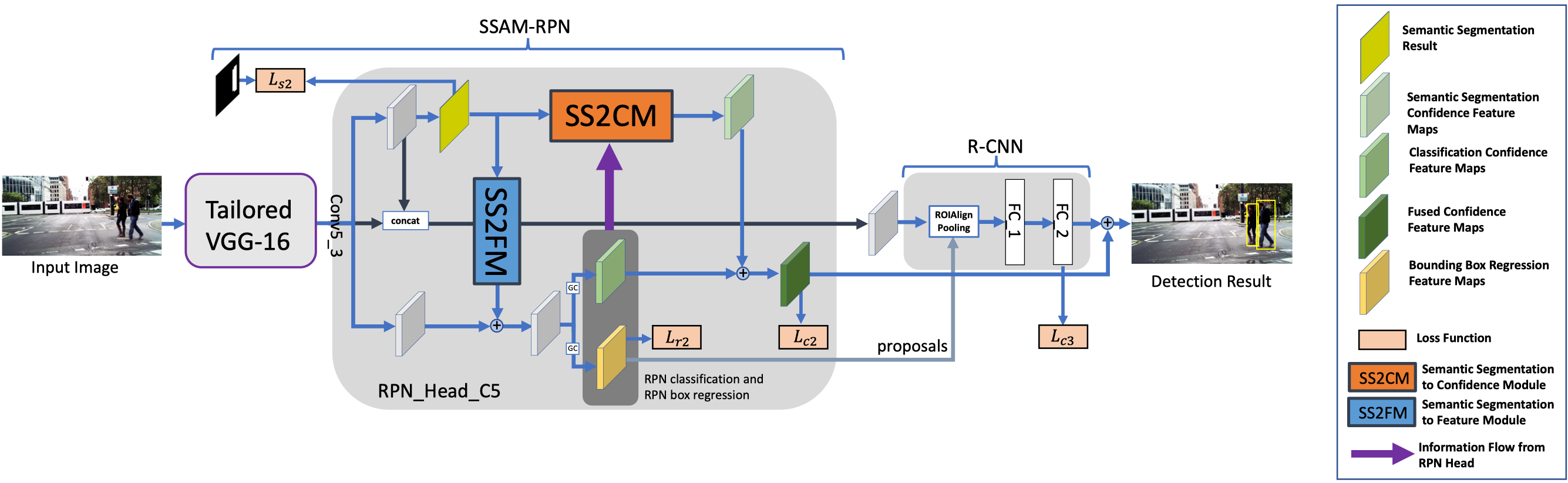
This work was supported in part by the National Research Foundation Singapore under its Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) Program with the Technical University of Munich at TUMCREATE.
Publications
- Chengju Zhou, Meiqing Wu, and Siew-Kei Lam, “A Unified Multi-task Learning Architecture for Fast and Accurate Pedestrian Detection”, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems [PDF]
- Chengju Zhou, Meiqing Wu, and Siew-Kei Lam, “Group Cost-sensitive BoostLR with Vector Form Decorrelated Filters for Pedestrian Detection”, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Vol. 21, No. 12, December 2020 [PDF]
- Chengju Zhou, Meiqing Wu and Siew-Kei Lam, “Fast and Accurate Pedestrian Detection using Dual-Stage Group Cost-Sensitive RealBoost with Vector Form Filters”, 25th ACM Multimedia (MM), October 2017 [California, USA] [PDF]
- Chengju Zhou, Meiqing Wu and Siew-Kei Lam, “Group Cost-sensitive Boosting with Multi-scale Decorrelated Filters for Pedestrian Detection”, 28th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), September 2017 [London, UK] [PDF]
Context-Aware Pruning for Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation, which predicts a semantic label for all pixels in the given image, plays a vital role in applications such as autonomous driving and robot navigation. However, most state-of-the-art models have low speed and require large memory storage. Network pruning for deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) has recently achieved notable research progress on image-level classification. However, most existing pruning methods are not catered to or evaluated on semantic segmentation networks.
The proposed Context-aware Pruning (CAP) framework performs network pruning to remove the parameter redundancy of deep neural networks for semantic segmentation. Different from existing pruning methods, the proposed framework exploits contextual information to guide the channel pruning. We formulated the embedded contextual information by leveraging the layer-wise channels interdependency via the Context-aware Guiding Module (CAGM) and introduce the Context-aware Guided Sparsification (CAGS) to adaptively identify the informative channels on the cumbersome model by inducing channel-wise sparsity on the scaling factors in batch normalization (BN) layers.
The resulting pruned models require significantly lesser operations for inference while maintaining comparable performance to (at times outperforming) the original models. We evaluated our framework on widely-used benchmarks and showed its effectiveness on both large and lightweight models.
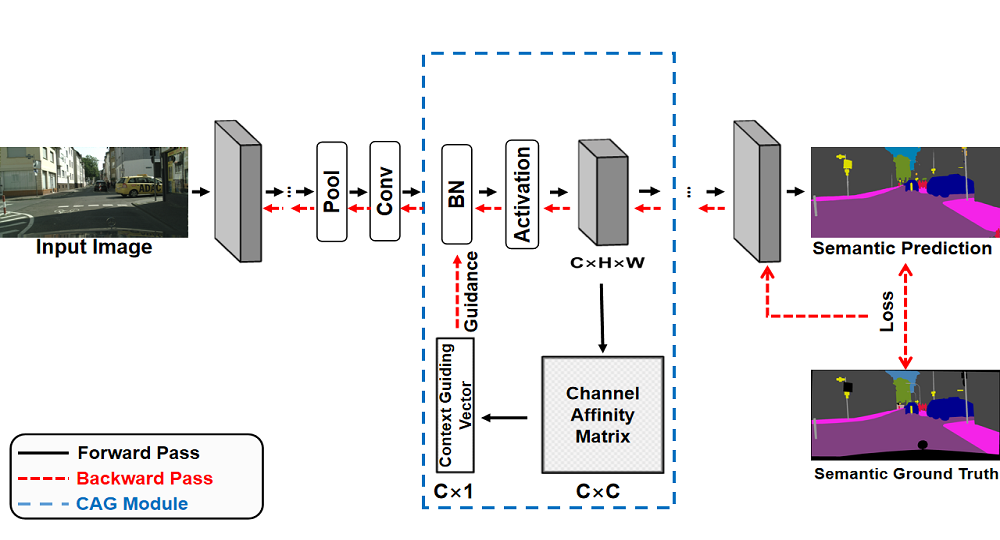
This work was supported in part by the National Research Foundation Singapore under its Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) Program with the Technical University of Munich at TUMCREATE.
Publications
- He Wei, Meiqing Wu and Siew-Kei Lam, “CAP: Context-Aware Pruning for Semantic Segmentation”, IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), January 2021 [PDF]



